Proudly Serving 25+ Brands
Proudly Serving 25+ BrandsBuilding Scalable Digital, Marketing & Sports Solutions for Global Businesses
Togwe is a global AI-powered services company delivering gaming platform development, performance marketing, digital growth, operations, and sports-focused solutions.
We help businesses launch, scale, and optimize high-performance platforms with measurable results.
Get a Free Consultation
AI-driven solutions powering gaming,sports,and digital growth at scale.
We build AI-powered systems that drive real performance across gaming, sports, and digital platforms. From smarter engagement to scalable growth, our solutions are engineered for speed, accuracy, and impact.
Explore our Services
Sports App Development
Secure, scalable platforms built for performance and growth.
Digital Marketing
Intelligent user acquisition, optimization, and revenue growth.
Content Creation
Data-informed content that drives engagement and brand recall.
Customer Support
AI-assisted support workflows for faster resolution and retention.
Branding & Advertising
Insight-led branding and measurable advertising outcomes.
Sports Sponsorship Management
Data-backed sponsorships and long-term partnerships.
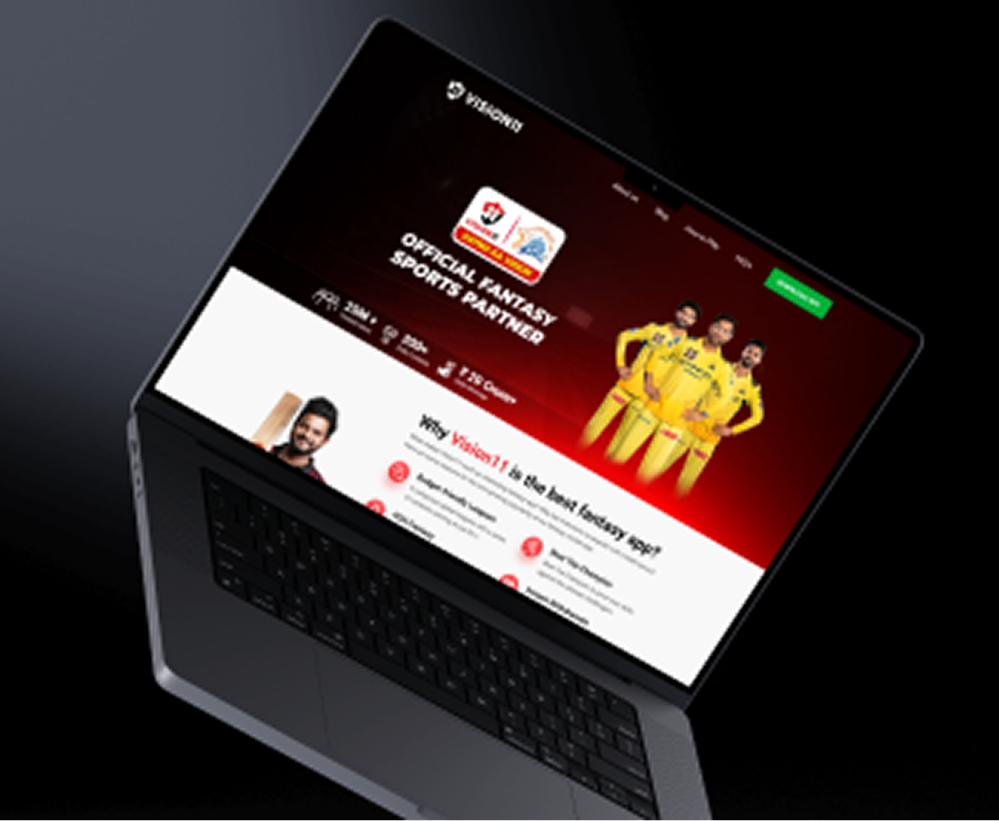
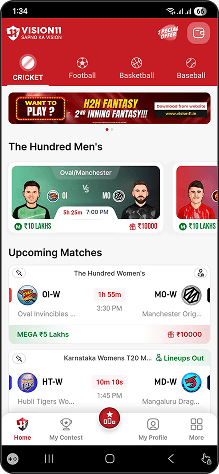
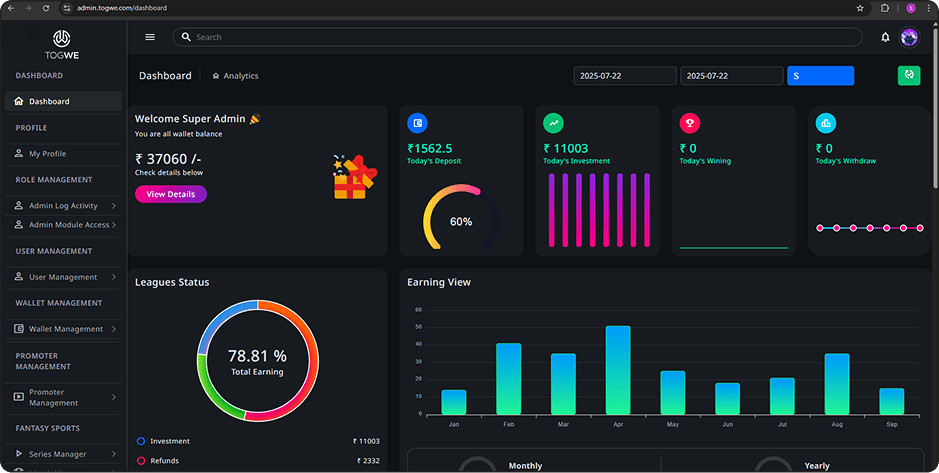
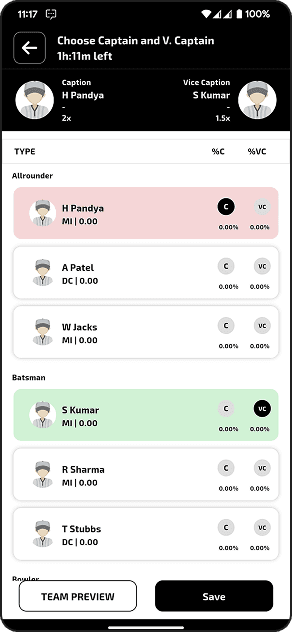
Glimpse of Mobile & Web Apps
A Glimpse of Your Next
Sport Platforms in Action
Take a tour through our sports app’s interface and see how every screen is thoughtfully designed for performance, clarity, and user satisfaction.















Who we are?

Togwe is a global services company operating at the intersection of gaming, technology, marketing, operations, and sports. We partner with platforms, organizations, and enterprises to deliver practical, scalable, and performance-focused solutions that support long-term growth.
We don’t offer generic services — we build systems, execution models, and partnerships that scale.
Our Values
Transparency
Clear communication, honest execution, and measurable outcomes
Performance
Every solution is designed to drive efficiency, growth, or engagement
Accountability
Ownership of execution, delivery, and results
Long-Term Growth
We focus on sustainable partnerships, not short-term wins
Growth
0%
Established
0
Successful Projects
0+
Users Impacted
0M+
Who We Work With
We partner with organizations that value performance, scalability, and long-term growth.
- Established businesses and enterprise teams
- High-growth companies scaling globally
- Sports organizations and ecosystem partners
- Digital-first brands with complex operations
- Innovation-led companies seeking measurable results
Our clients






Agile. Transparent. Built to Scale.
We follow an Agile-driven development and growth model designed for gaming platforms, where speed, performance, and continuous improvement are critical.
1. Discovery &
Strategy
2. Product &
Experience Design
3. Agile Development
(Sprint-Based)

4. Testing, Security &
Performance
5. Launch & Growth
Enablement
6. Scale, Optimize &
Evolve
Our Case Study
We aren’t just all talk company—rather we are go and build it experts. Take a look at our portfolio of successful projects.
Togwe has been recognized for delivering top-quality IT solutions and marketing services to businesses across the globe.





Take a look at what our past clients say about our mobile app development and other services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Insights That Power Growth
Explore articles on gaming platforms, AI-powered technology, digital natives, and performance marketing - designed to help you get ahead in the fast-paced digital design world.
How Online Gaming Companies Add Payment Gateways on Their Websites: A Complete Guide
The online gaming industry has seen tremendous growth over the past decade. For these platforms to function smoothly, one critical component must function flawlessly: the payment system. Players expect to deposit money instantly, join competitions without delay, and withdraw their winnings securely. This is where payment gateways play a vital role. A payment […]
![List of Brands Endorsed By Shikhar Dhawan [2026 Updated]](https://www.togwe.com/backend/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/brands-endorsed-by-shikhar-dhawan.webp)
List of Brands Endorsed By Shikhar Dhawan [2026 Updated]
Shikhar Dhawan has been a prominent face in the world of endorsements till 2026. He has the energy that brands want and brings a kind of easy charm that reads well on screen and in print. His partnerships span sportswear, technology, FMCG, grooming and lifestyle. He is for the youth and those who […]
![List of Brands Endorsed By Rohit Sharma [2026 Updated]](https://www.togwe.com/backend/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/brands-endorsed-by-rohit-sharma.webp)
List of Brands Endorsed By Rohit Sharma [2026 Updated]
As of 2026, Rohit Sharma is one of India’s most marketable cricketers. The calm nature he brings to captaincy is what carries him over into the commercial world. Brands seek him out because his image is stable and familiar. He is not a one-off. He is a man who has earned a place […]